The way developers build software is quietly changing.
Developers are making a strategic shift, embracing open-source tools that offer something far more valuable: genuine control and transparency.
As we approach 2026, clear patterns are emerging across developer communities, open-source repositories, and day-to-day workflows. Tools that prioritize local-first development, privacy, performance, and community ownership are gaining steady traction, especially among independent developers & teams looking to avoid vendor lock-in.
These selections are based on observable trends such as growing community activity, active development, increasing mentions in developer discussions, and their alignment with how modern software development is evolving. These tools represent where development is realistically heading and why they matter going into 2026.
1. Ollama: Local AI for Developers

AI-assisted development is rapidly becoming part of everyday workflows, but many developers are increasingly uncomfortable sending proprietary code, prompts, or project context to cloud-based AI services. Ollama addresses this concern by enabling developers to run large language models locally on their own machines.
Ollama simplifies working with open-source LLMs by handling model downloads, updates, and execution through a clean and developer-friendly interface. It integrates smoothly into existing development environments, making local AI experimentation practical rather than complex.
Some Powerful features of OLLAMA that makes it stand out:
- Run powerful language models completely offline
- Maintain full control over code and data privacy
- No API rate limits or recurring usage costs
- Ideal for experimentation, prototyping, and local-first workflows
As privacy concerns, licensing uncertainty, and cloud dependency risks continue to grow, tools like Ollama represent a shift toward developer-controlled AI infrastructure. By 2026, local AI tooling is expected to become a normal part of modern development setups.
OLLAMA Github Repository: ollama
2. Hoppscotch: API Development Ecosystem

Hoppscotch is an open-source API development and testing tool built for speed, simplicity, and flexibility. It’s often seen as a lightweight yet powerful alternative to heavier API clients, making it especially appealing for developers who prefer minimal tooling without sacrificing functionality.
1. Extremely Fast & Lightweight
Hoppscotch launches almost instantly, whether used in the browser or self-hosted. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for quick API testing, debugging, and experimentation without slowing down your development workflow.
2. Fully Open Source & Self-Hostable
Being completely open source, Hoppscotch allows developers to self-host their own instance, maintain full control over data, and avoid dependency on proprietary cloud services.
3. Multi-Protocol API Support
Hoppscotch goes beyond basic REST APIs and supports:
- REST
- GraphQL
- WebSocket
- Server-Sent Events (SSE)
- MQTT
This makes it a versatile tool for modern backend and real-time applications.
4. Clean, Developer-Friendly Interface
Its minimalist UI is designed to reduce clutter while keeping essential features easily accessible, allowing developers to focus on testing APIs instead of navigating complex menus.
5. Collaboration & Environment Management
Hoppscotch supports environment variables, collections, and request sharing, enabling smoother collaboration across teams and projects.
Hoppscotch Github Repository: Hoppscotch
3. Supabase

Modern application development often requires managing databases, authentication, APIs, storage, and real-time functionality—all of which can quickly increase complexity. Supabase addresses this by offering an open-source backend platform that helps developers build production-ready applications without reinventing core infrastructure.
Supabase simplifies backend development by providing instant APIs, authentication, file storage, and real-time capabilities on top of PostgreSQL. Its developer-first approach allows teams to move faster while still working with familiar, industry-standard technologies rather than proprietary abstractions.
Some powerful features of Supabase that make it stand out:
- Built on PostgreSQL with full SQL support
- Automatic REST and real-time APIs from database schemas
- Flexible authentication with multiple providers
- Open-source and self-hostable architecture
- Scales from small projects to enterprise-grade applications
As developers seek alternatives to closed backend platforms and vendor lock-in, tools like Supabase represent a shift toward transparent, open, and scalable infrastructure. By 2026, open-source backend platforms are expected to play a central role in modern web and application development.
Supabase GitHub Repository: supabase
4. Dyad
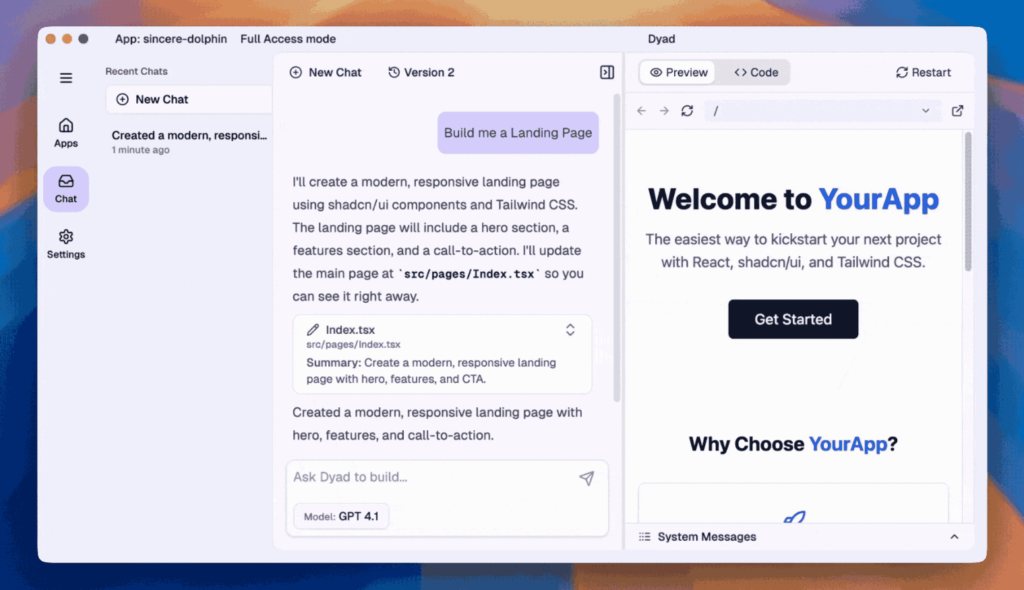
Application development increasingly demands full control, privacy, and flexibility. Dyad addresses this by letting developers build unlimited AI-powered applications locally, without being locked into a single vendor or cloud service.
Dyad integrates with Supabase to provide authentication, databases, and server functions, allowing developers to create full-stack applications including MVPs directly within the platform. Its design emphasizes local-first development, giving developers complete control over their source code while maintaining compatibility with their favorite IDEs.
Some powerful features of Dyad that make it stand out:
- Build full-stack apps locally with Supabase integration
- Support for any AI model, including Gemini 2.5 Pro, GPT-5, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and more
- Complete code ownership: your tools, your workflow
- Local execution for privacy, speed, and smooth development experience
- Fast, responsive interface with real-time previews and frictionless testingaa
As AI-driven development grows, tools like Dyad represent a shift toward empowering developers with local-first, flexible, and vendor-independent solutions. By 2026, local AI application development is expected to become a core part of modern workflows.
Dyad GitHub Repository: dyad
Also Read: Top 25 Offline AI Tools to Automate Tasks and Boost Productivity
5. Neovim
Neovim is redefining what developers expect from a text editor. By building on Vim’s core strengths while modernizing its architecture, Neovim allows developers to work faster, automate more tasks, and extend their environment without being restricted by the editor itself.
It introduces a refactored codebase, asynchronous job control, and wide-ranging API access, enabling custom workflows across multiple programming languages and environments. Its focus on performance, modularity, and extensibility makes it a favorite for developers who demand both power and flexibility in their tools.
Features of Neovim include:
- Support for modern GUIs and embedded terminal emulators
- APIs accessible from languages like Lua, Python, Rust, JavaScript, Go, and more
- Asynchronous job execution for smooth multitasking
- Shared data (shada) across multiple instances to maintain consistent workflows
- Full compatibility with most Vim plugins, including Ruby and Python plugins
- Support for XDG base directories for better system integration
Neovim’s combination of performance, extensibility, and plugin ecosystem positions it as a modern editor for developers who want complete control over their development environment. By 2026, Neovim is expected to remain a cornerstone for developers seeking lightweight, customizable, and efficient editing tools.
Neovim GitHub Repository: neovim
6. Podman
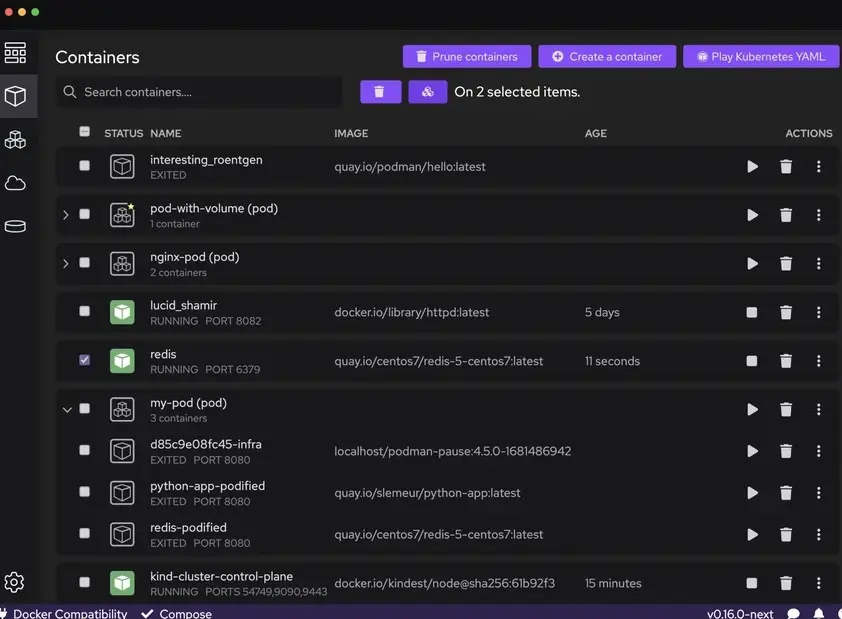
Containerization has become a core part of development and deployment, but many teams are looking for more secure, lightweight, and daemon-free alternatives to traditional container tools. Podman addresses this by providing a powerful container and pod management solution built around security, flexibility, and standards compliance.
Podman allows developers to manage OCI-compatible containers, images, volumes, and pods without requiring a long-running daemon. Its architecture improves security, reduces idle resource usage, and makes container workflows more transparent—especially in Linux-based and enterprise environments.
Some powerful features of Podman that make it stand out:
- Daemonless container architecture for better security and lower resource usage
- Full support for OCI and Docker-compatible container images
- Rootless containers that run without elevated privileges
- Native pod support for managing groups of containers together
- Docker-compatible CLI for easy migration
- Works on Linux natively and on macOS/Windows via Podman-managed virtual machines
- REST API support for automation and advanced integrations
Podman’s focus on rootless execution, standards compliance, and security-first design has made it a strong choice for developers and DevOps teams moving beyond traditional container setups. By 2026, daemonless and rootless container tools like Podman are expected to play an even bigger role in production-grade container workflows.
Podman GitHub Repository: Podman
7. Deno

JavaScript runtimes have long been powerful, but they often rely on complex tooling, external bundlers, and permissive security models. Deno approaches this differently by offering a modern runtime designed around security, simplicity, and first-class TypeScript support.
Built on V8, Rust, and Tokio, Deno provides a smooth developer experience with sensible defaults. It removes the need for many third-party tools by supporting TypeScript out of the box, enforcing explicit permissions, and offering a streamlined way to build servers, scripts, and modern web applications.
Some powerful features of Deno that make it stand out:
- Secure-by-default permission system for network, file, and environment access
- Native TypeScript and WebAssembly support without extra configuration
- Single executable with built-in tooling like formatting, linting, and testing
- Modern standard library and JSR package registry
- Designed for building fast web servers and backend services
As developers seek cleaner, safer, and more predictable JavaScript runtimes, Deno represents a move toward simplified and secure development workflows. By 2026, runtimes with strong defaults and built-in tooling like Deno are expected to play a major role in modern backend and edge computing environments.
Deno GitHub Repository: deno
8. OpenTofu

Managing infrastructure manually doesn’t scale, especially as systems grow across multiple cloud providers and internal platforms. OpenTofu addresses this challenge by providing a fully open-source way to define, manage, and evolve infrastructure using code.
OpenTofu allows teams to describe infrastructure through a declarative configuration language, making environments reproducible, reviewable, and version-controlled just like application code. It supports popular cloud providers as well as custom in-house solutions, giving organizations flexibility without sacrificing control.
Some powerful features of OpenTofu that make it stand out:
- Infrastructure as Code approach for safe, versioned, and reusable setups
- Execution plans that clearly show what will change before applying updates
- Resource graph that understands dependencies and applies changes efficiently
- Parallel resource creation for faster infrastructure provisioning
- Change automation that reduces manual errors during complex updates
As organizations move toward auditable, automated, and transparent infrastructure workflows, tools like OpenTofu represent a growing shift toward open-source infrastructure management. By 2026, community-driven IaC tools are expected to become a core part of modern DevOps and platform engineering practices.
OpenTofu GitHub Repository: opentofu
Also Read: 12 Free Desktop Apps I Wish I Discovered Sooner: Must-Haves for 2026
9. Nix

Managing software dependencies consistently across machines has always been a challenge, especially as projects grow more complex. Nix approaches this problem by redefining how packages are built, installed, and shared focusing on reliability, reproducibility, and isolation.
Nix allows developers to describe packages and development environments declaratively, ensuring that the same configuration produces the same result every time. This makes it especially valuable for teams that want to eliminate “it works on my machine” issues while maintaining flexible, versioned setups across systems.
Some powerful features of Nix that make it stand out:
- Reproducible builds using a purely functional package model
- Isolated package installations with no dependency conflicts
- Ability to install and use multiple versions of the same package simultaneously
- Declarative development environments that can be shared across teams
- Backed by Nixpkgs, one of the largest free software repositories in the world
Originally created by Eelco Dolstra as part of his PhD research, Nix has grown into a mature ecosystem supported by a global developer community. As reproducibility and long-term maintainability become increasingly important, tools like Nix are expected to play a key role in modern development workflows by 2026.
Nix GitHub Repository: Nix
10. OpenCode

Developers are increasingly integrating AI-assisted coding, but they often struggle to find a tool that works easily across terminals, IDEs, and desktops. OpenCode Desktop addresses this need by offering an open-source AI coding agent that integrates smoothly into any environment while keeping code fully private.
OpenCode supports multiple LLMs, including GPT, Claude, Gemini, and over 75 other models, allowing developers to experiment with different AI tools without being locked into a single provider. Its desktop app is available in beta for macOS, Windows, and Linux, making AI coding assistance accessible across platforms.
Some powerful features of OpenCode Desktop that make it stand out:
- Run AI coding agents locally or connect to cloud models without sending code externally
- Multi-session support: start multiple agents on the same project in parallel
- Shareable session links for debugging or reference
- LSP-enabled: automatically loads the right language servers for your chosen model
- Compatible with any editor: terminal interface, desktop app, or IDE extension
- Privacy-first: does not store any code or context data
OpenCode is trusted by over 400,000 developers every month, as per official stats, demonstrating its growing adoption in the developer community.
OpenCode GitHub Repository: OpenCode
Wrapping Up
The landscape of developer tools is evolving rapidly, with a clear shift toward local-first, privacy-focused & highly extensible solutions.
These open-source solutions are not just “nice-to-have”, they are shaping the way modern development is done, helping developers build, test, and deploy software faster, more securely, and with greater confidence. By exploring and integrating these tools into your workflow, you’re staying ahead of the curve and ready for the innovations of 2026 and beyond. Which of these tools will become an essential part of your dev toolkit? The choice is yours & the future is open.


